In general, the following methods can be used individually or in a combined form to stabilize excavations:
In each of the above methods, due to design requirement, a retaining wall element might be needed. This element can be diaphragm walls, tangential concrete piles, jet grouting and deep mixing columns, steel soldier piles, sheet piles or similar elements. In a nailing method, a shotcrete layer is usually used as a wall facing.
![]() See more our nailing and projects…
See more our nailing and projects…
 See our scientific database to learn more about nailing and achorage…
See our scientific database to learn more about nailing and achorage…
Each of retaining wall system has it’s own advantage and limitations that can be considered in a design. In addition to the technical and construction considerations, following figure shows a comparison of the cost of the implementation of different retaining wall system via excavation’s depth.
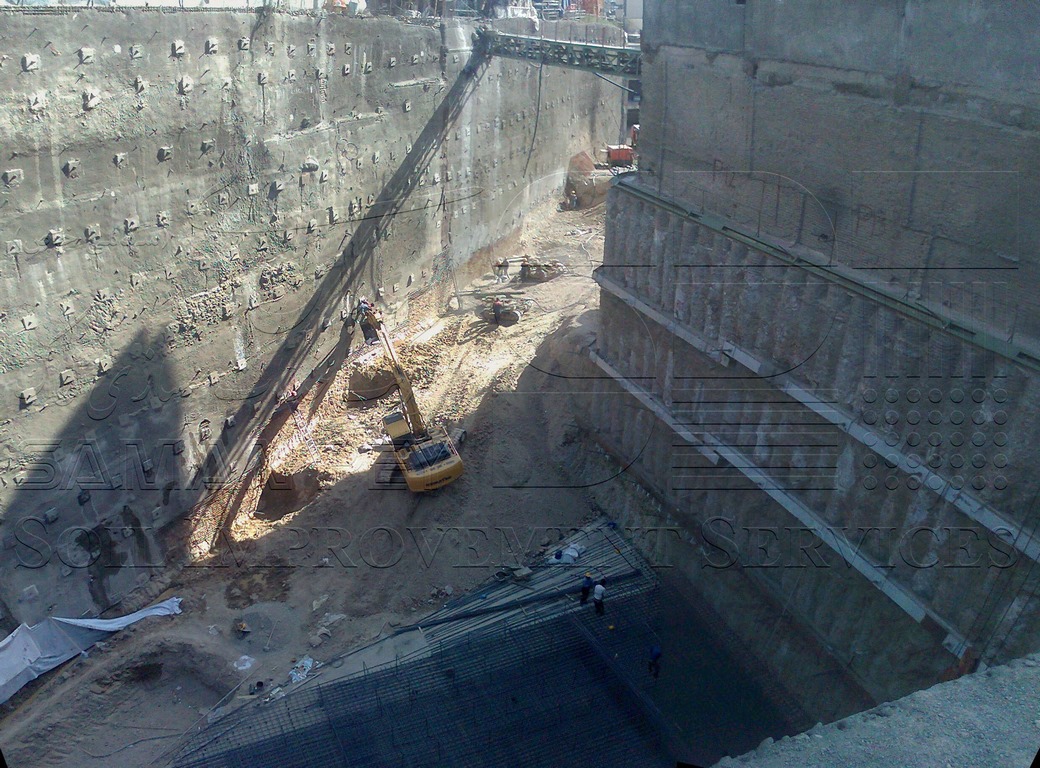

Combination of excavation stabilization systems
Price comparison between different retaining wall methods (ICE Manual of Geotechnics, 2012)
Element types for retaining wall construction
Soil nailed walls or nailing is an in-situ reinforcement method with installed steel bars that retains an top to bottom excavated wall. Bars are usually installed in boreholes located on the wall of the earth, which are filled with cement grout in order to prevent corrosion of the bar and proper transfer of forces between the soil body and bar. This operation provides a stable reinforced wall that has the ability to retain soil.
This method was first discussed in 1960. Soil nailing is based on the method of rocks anchorage. For the first time, this stabilization system was used for tunneling in Australia in 1960. In this tunnel, steel bar reinforcement, injected cement grout and shotcrete was used to for tunnel stabilization. In the next years, this technique spread over the world. In Iran, use of this method has developed considerably in recent years and is one of the most practical methods, especially in urban construction.
In scientific principles of geotechnical engineering, soil nailing method acts in a passive manner and applies it’s effect through the interaction of soil-reinforcement due to the appearance of deformation in the soil. Hence, the use of a soil nailing system in situations where the sensitivity to the displacement caused by the excavation is high or in the vicinity of sensitive and old structures, or in soft and medium hardened soils, is not recommended generally.
Soil nailing is a new method which, due to its economic and unique advantages, is considered as a very suitable solution in various cases, such as stabilization of slopes and trenches, increasing load capacity and limiting changes in earth surface by projects. The use of this soil reinforcement method has been widely used in most of the developed and developing countries in the last two decades to stabilize excavations and natural slopes. Some of the vast applications of this method of soil reinforcement is to include the stabilization of natural slopes and/or trenches adjacent to the roads, expansion of roads, excavation in the vicinity of existing structures, stabilization and retrofitting of old retaining structures.
Soil nailing wall construction stages
Nails often act in tension, but in certain conditions, their flexural and shear performance is also considered. The effect of nail reinforcement effect to improve wall stability is achieved through two functions:
After bar instalation, a thin surface wall, usually containing shotcrete with lightweight steel layer as a steel mesh, covers the surface of the wall. The purpose of this soil nailed wall is to prevent surface erosion of the soil and making this surface more suitable for possible future construction.
The more important goal of the construction of these walls is to increase the efficiency of the consolidated soil system, especially in parts close to the excavation wall. Concrete-steel layer (Reinforced shotcrete) also makes a better transfer of forces to reinforcement elements. The facing can be designed and constructed temporarily or permanently. Principles of the interacting behavior in soil nailed walls shown in figure.
Behavior principles of soil nailed walls
Principles of anchorage method construction are similar to the nailing method. The main difference is in the application of post-stress force applied to the reinforcement element. Construction steps are similar to the soil nailing, including cross-sectional excavation, boreholes drilling, installting of reinforcing bars, injection of cement grout(on the part of the borehole length), concrete spraying (shotcrete), and installation of the plate and the nut. After the curing period of cement grout, post-tension force will be applied to the desired amount of design to the bar.
Construction process of soil anchorage method is presented schematically in figure. In the first stage, a retaining wall is constructed. In the second stage of excavation, the first rows of anchors are set up. In the third stage, drilling borehole is done for anchors installation. In the fourth stage, grout injection is carried out in and in the fifth step after the grout curing, shotcrete layer will be constructed. In this stage, it is also possible to implement a permanent cover as needed. These facings can also be sprayed concrete (shotcrete), prefabricated concrete, in-situ concrete and other newer types of technologies for the implementation of environmental friendly designs. In anchorage method, there are a variety of injection methods available to supply the bond resistant.
Soil anchorage construction stages
In this method, pressure bearing elements are used for transferring soil pressure. The components of this system generally include a wall that can be Sheet Pile type, a diaphragm wall, a metal or concrete soldier wall, etc. The compression members are called Strut or Brace, and members are between the walls and pressure members called Wale.
In this method, soil pressure is transmitted through the wall to the Wale and via Wale to the Struts. As a result, Struts and their connection are designed based on the compression force, an the Wale’s are designed based on the shear and flexural force and the wall is designed based on the combined forces.
In this method, the soldier piles are executed as a temporary wall, and then each stage of the Wale and the Struts connected to them, will be constructed.
In this method, 2D or 3D modeling can be used to control the ultimate and serviceability states and design of the structural members on the basis of the forces involved. Structural members are generally steel and are designed in accordance with the rules of steel structures.
Braced excavation (Struts) system components
In this method, instead of constructing a seprated excavation structure, the main structure is performed from top to bottom, and simultaneously excavation is done. The executive steps are generally shown in the figure. This method, was used in the construction of subway stations in Europe in order to reduce time and cost of the operation, reduce the disruption of urban traffic by making changes to the design and calculation of the structure. Due to its high benefits in recent years in large-scale projects this method have practically replaced traditional construction methods.
Excavation construction is traditionally known as the Bottom-Up method, and ends with reaching to the final depth and then the foundation’s construction will be start ed and ends with the construction of the main structure.
Unlike the above-mentioned method, Top-Down method is existed, which in recent years has actually replaced in large projects. This method, in contrast to the traditional method, is based on the construction of round walls, columns, and ceiling, and completes the excavation and construction of the structural foundation. One of the main advantages of this method can be mentioned by reducing the temporary anchorage elements.
Top-down construction stages
In this method, the diaphragm wall is first installed in the perimeter. After that, the structural columns with a deep or semi-deep pile foundation are constructed and top-down structures are constructed simultaneously with the excavation, respectively. If the condition of the soil is suitable for the strength and the sub-surface water conditions are favorable, the wall can also be performed in a step-by-step while the floors are constructed from top to bottom.
In this method, the whole structure or part of it can be implemented as top-down (TD). If the dimensions of the project are small in size, the implementation of the entire underground structure is easily possible with the TD method. It is also possible to combine this method with other methods of stabilization.
Results of using instrumentation systems for monitoring and measurement, can mention the following:
In addition to monitoring, quality control of the components of the retaining structure is also very important during construction. Controlling the implementation of the retaining structure can be specified by testing the quality of concrete, reinforcement bars and all materials.
Excavation monitoring instruments